Grow Your Green Oasis: Timberlake Raised Garden Beds with Greenhouses
- Staff Desk
- Sep 26
- 20 min read
Updated: Sep 29

Planning Your Timberlake Raised Garden Bed with Greenhouse
Choosing the perfect Location: Sunlight, Soil, and Accessibility
Sunlight is paramount for a thriving Timberlake raised garden bed and greenhouse combination. Most vegetables require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. In our experience, south-facing locations (in the Northern Hemisphere) generally receive the most sun, but you should carefully observe your yard’s sunlight patterns throughout the day before settling on a spot. Consider using a sun tracking app or simply marking the sun’s position at various times over several days to determine the optimal placement. A common mistake we see is overlooking the impact of nearby trees or buildings, which can cast significant shade during parts of the day.
Soil quality significantly impacts plant growth. While raised beds offer control over soil composition, careful consideration of the existing soil is still crucial. Ideally, the area should drain well; poor drainage can lead to root rot and other plant diseases. Before installing your beds, test the soil pH. Most vegetables prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0-7.0). Amendments like compost or peat moss can adjust the pH if necessary. You should also consider soil depth, as some plants have extensive root systems requiring a deeper soil profile than others.
Accessibility is key for efficient gardening. Locate your Timberlake raised garden bed and greenhouse where you can easily reach them. This includes considering proximity to a water source for irrigation, as well as convenient access for planting, harvesting, and maintenance. Think about the path to your beds—is it easily navigable, even when carrying heavy loads or in inclement weather? We’ve seen many enthusiastic gardeners select beautiful but impractical locations. Remember to consider the overall layout and flow of your garden space for maximum functionality and ease of use. Prioritizing accessibility from the outset will save you time and effort in the long run.

Designing Your Ideal Greenhouse Structure: Size, Shape, and Material
Determining the optimal greenhouse size hinges on your gardening ambitions and available space. A common mistake we see is underestimating the necessary square footage. In our experience, starting with a 6′ x 8′ greenhouse provides ample room for a variety of plants, even with multiple raised beds. However, consider expanding to 8′ x 12′ or larger if you plan on extensive cultivation or year-round growing. Remember to account for walkways and ease of access to all your plants.
Shape significantly impacts light penetration and internal airflow. While gable roofs offer superior headroom and ventilation, hoop houses are more affordable and easier to erect, especially for DIY projects. The choice depends on your budget, DIY skill level, and regional climate. For example, in regions with heavy snowfall, a stronger gable design might be preferable to minimize structural stress. Conversely, in milder climates, the cost-effectiveness of a hoop house might be a better fit.
Material selection is crucial for longevity and climate control. Polyethylene film offers a budget-friendly option but is less durable and needs replacing every few years. Polycarbonate panels, on the other hand, are more expensive but provide superior insulation, light transmission, and longevity, often lasting a decade or more. Glass green houses are beautiful and provide excellent light transmission, but their cost and fragility limit their practicality for many gardeners. Consider your budget, maintenance preferences, and local climate when choosing your greenhouse material for your Timberlake raised garden bed system.
Selecting the Right Timberlake for Your Project: Durability and Aesthetics
Choosing the right timber for your raised garden bed and greenhouse combination is crucial for longevity and aesthetic appeal. In our experience, the most common mistake is overlooking the specific needs of your climate. For example, cedar, renowned for its natural rot resistance, thrives in drier climates but may require more frequent treatment in consistently damp environments. Conversely, redwood, while also naturally durable, can be more expensive but offers exceptional longevity, especially when properly sealed.
Consider the durability factors beyond inherent rot resistance. Heartwood, the denser inner portion of the tree, significantly outperforms sapwood in terms of lifespan and resistance to insect damage. Look for lumber graded specifically for outdoor use, indicating that it’s less prone to warping and cracking. Pressure-treated timber offers a cost-effective alternative, but be mindful of the chemicals used; ensure they are safe for your plants and soil. A common choice is pressure-treated pine, offering a good balance of affordability and durability. However, always check the treatment specifics to confirm plant compatibility.
Finally, consider the aesthetic impact. The natural beauty of untreated cedar or redwood complements many garden styles, creating a rustic charm. However, these woods will weather over time, developing a silvery-grey patina. If you prefer a consistent color, staining or sealing is recommended. Pressure-treated pine can be painted to match your existing structures, offering a more uniform look. Ultimately, the best timber choice depends on your budget, climate, maintenance preferences, and overall design vision. Weighing these factors carefully will ensure a beautiful and long-lasting raised garden bed and greenhouse structure.

Gathering Materials and Tools: A Comprehensive Checklist

Timberlake Selection: Sourcing Sustainable and High-Quality Lumber
Choosing the right timber for your raised garden beds is crucial for longevity and structural integrity. In our experience, cedar and redwood are top choices due to their natural resistance to rot and decay, extending the lifespan of your beds significantly. However, the cost can be higher than other options. Pressure-treated lumber is another possibility, but be aware that the chemicals used can leach into the soil, potentially affecting plant health. Always opt for lumber treated with copper azole, which is less harmful to plants and the environment.
When sourcing your lumber, prioritize sustainability. Look for certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) logo, guaranteeing the wood comes from responsibly managed forests. A common mistake we see is neglecting to check the moisture content. Ideally, aim for lumber with a moisture content of 15% or less to minimize warping and cracking. Inspect each board carefully for knots, splits, and other imperfections. Larger knots, while adding character, can weaken the structural integrity of your raised bed, especially if positioned at critical stress points.
Consider the dimensions carefully. For example, 2×6 lumber provides a robust build, suitable for larger beds and taller plants. Thinner boards might suffice for smaller, shallower beds but will necessitate more frequent maintenance. Remember, pre-cutting lumber to your desired lengths will save considerable time on-site. Purchasing from a local lumber yard allows for personal inspection and often provides helpful advice from experienced staff. This direct interaction offers invaluable insight, particularly regarding local wood sources and best practices for the climate.
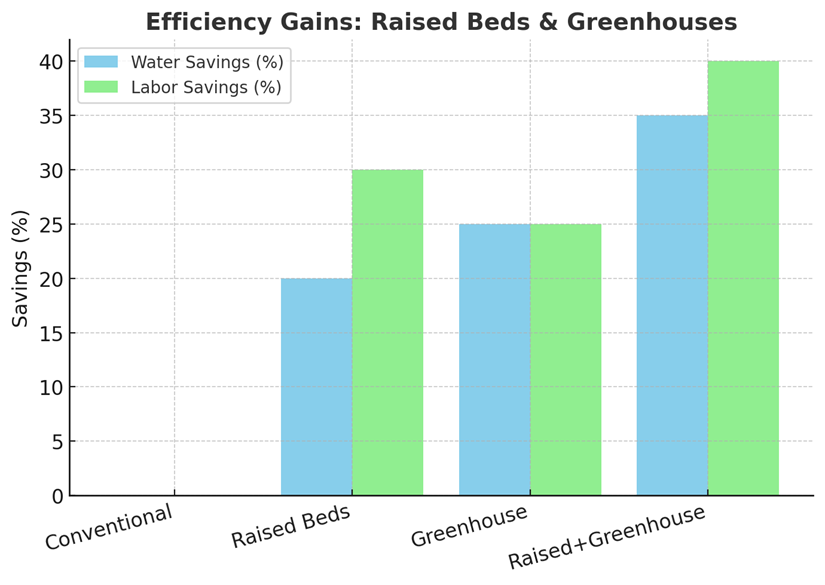
Greenhouse Materials: Glass, Polycarbonate, or Other Options
Choosing the right greenhouse glazing material significantly impacts your Timberlake raised garden bed’s performance and longevity. The three most popular choices are glass, polycarbonate, and polyethylene film. In our experience, glass offers superior light transmission, typically around 90%, fostering optimal plant growth. However, it’s heavier, more fragile, and significantly more expensive than alternatives. Consider its suitability based on your budget and the potential for strong winds or hail in your area.
Polycarbonate sheets present a compelling middle ground. They boast excellent light transmission (around 85%), are significantly stronger and lighter than glass, and offer superior insulation, reducing energy costs for heating in colder climates. A common mistake we see is underestimating the impact of UV degradation on polycarbonate; opting for UV-resistant panels is crucial for long-term performance. Furthermore, polycarbonate comes in various thicknesses, influencing both strength and cost. Thicker panels are more durable but also more expensive.
While polyethylene film is the most budget-friendly option, its lifespan is considerably shorter than glass or polycarbonate, usually lasting only a few seasons. Light transmission is also lower, often around 75%, and its susceptibility to tearing limits its practicality, especially in regions with harsh weather conditions. We recommend polyethylene film only for temporary setups or extremely budget-conscious projects. Ultimately, the best greenhouse glazing material depends on your specific needs, climate, budget, and the desired lifespan of your structure.
Essential Tools: From Measuring Tapes to Power Drills
Accurate measurements are paramount for successful Timberlake raised garden bed construction. In our experience, a high-quality measuring tape (at least 25 feet long) is essential, alongside a level to ensure your beds are perfectly plumb. Don’t skimp here; a wobbly bed compromises drainage and structural integrity. We’ve seen numerous projects hampered by inaccurate measurements, resulting in wasted materials and frustrating rebuilds.
Beyond measuring, you’ll need tools for assembly. A power drill with various drill bits (including those appropriate for the chosen wood type) is indispensable. Pre-drilling pilot holes is crucial, especially for hardwoods like cedar or redwood; this prevents splitting and ensures clean, strong joints. Consider a impact driver for quicker and easier screwing. Further, a circular saw will be necessary for cutting lumber to size, and a jigsaw offers more precise cuts for intricate shaping. Always prioritize safety – wear appropriate safety glasses and hearing protection.
Finally, for optimal construction and finishing touches, add these tools to your arsenal: a safety saw, clamps (various sizes for secure joining), a square (for accurate angle checking), a hammer, screwdrivers (both Phillips and flathead), and sandpaper for smoothing rough edges and splinters. choosing the right tools not only speeds up the process, but also ensures a professional-looking and long-lasting Timberlake raised garden bed, ready to nurture your flourishing green oasis. A common mistake we see is underestimating the need for clamps; they significantly improve the speed and accuracy of assembly.
Step-by-Step Construction Guide: Building Your Raised Garden Bed
Creating the Frame: Precision Cuts and Assembly Techniques
Precise cuts are paramount for a sturdy and visually appealing raised garden bed. In our experience, using a miter saw significantly improves accuracy compared to hand-cutting, especially when working with pressure-treated lumber. Pre-drill all pilot holes to prevent splitting, a common mistake we see, particularly with hardwoods. Remember to account for the thickness of your chosen wood when calculating cuts; a 1/2-inch difference can throw off the entire structure. For a 4×8-foot bed, for instance, using 2×6 lumber, the length of each side will not be exactly 8 feet.
Assembly techniques greatly influence the longevity and stability of your structure. We strongly recommend using galvanized exterior-grade screws; they’ll withstand the elements better than standard screws. When securing the corners, employ a robust joining method like a mortise and tenon joint for superior strength. This adds complexity but dramatically increases the structural integrity, especially for taller beds or those in areas with high winds. Alternatively, a simpler but effective approach involves using corner brackets in conjunction with screws. Ensure even spacing between boards, and don’t overtighten screws, which can cause warping.
Finally, consider pre-treating your lumber before assembly. Applying a water-resistant sealant prevents rot and extends the lifespan of your raised bed. Many options exist, from simple wood preservatives to more advanced, environmentally-friendly treatments. Remember to choose a product suitable for direct contact with soil if you intend to plant directly into the bed. A final coat of sealant after assembly will offer even greater protection against the elements and enhance the aesthetic appeal of your finished green oasis.
Adding Stability: Bracing and Reinforcing the Structure
Reinforcing your Timberlake raised garden bed is crucial for longevity and to withstand the weight of soil, plants, and potential weather stresses. In our experience, neglecting this step is a common cause of structural failure, leading to leaning walls and ultimately, a compromised growing space. We recommend using corner bracing as a foundational element. This involves installing strong, angled supports from the inside corners of the bed to the opposite sides, approximately a third of the way up the wall. These braces can be constructed from pressure-treated lumber, metal brackets, or even sturdy bamboo, depending on your aesthetic and budget. Consider using galvanized screws or bolts for superior durability against the elements.
Further strengthening can be achieved through strategically placed cross-bracing. This is especially important for larger beds or those in areas prone to strong winds. Imagine a grid system across the inside of the bed; these internal supports distribute weight effectively, preventing bowing and sagging. For instance, a 4ft x 8ft bed might benefit from two horizontal braces and two vertical braces. Remember to pre-drill holes to avoid splitting the wood during installation. A common mistake we see is using undersized bracing material. Overestimating the necessary strength ensures the structure withstands even the heaviest harvests and the occasional unexpected downpour.
Finally, consider the ground conditions. If your soil is particularly soft or prone to shifting, adding a robust base to your raised bed is essential. This could involve laying down a layer of gravel or compacted sand before assembling the structure. In addition to providing stability, this improves drainage, preventing waterlogging, a major problem for many raised bed gardeners. This extra layer of preparation provides a stable foundation, extending the lifespan and structural integrity of your Timberlake raised garden bed, ensuring a thriving growing environment for years to come.
Preparing the Foundation: Leveling and Soil Considerations
Leveling the ground is paramount for successful raised bed construction. In our experience, even a slight incline can lead to uneven water distribution and soil compaction, hindering plant growth. Use a landscape level and a shovel to meticulously remove or add soil, aiming for a perfectly flat base. A common mistake we see is rushing this step; take your time—it’s the foundation of your entire garden. Consider using string lines pegged at each corner to create a visual guide for maintaining a level plane.
Soil selection significantly impacts your garden’s success. While readily available topsoil might seem convenient, it often lacks the necessary drainage and nutrient profile for optimal plant health. We strongly recommend a blend specifically designed for raised beds; a typical mix might include 50% compost, 30% topsoil, and 20% perlite or coarse sand to improve drainage. Alternatively, consider creating a custom mix suited to your specific plants. For example, adding peat moss can increase water retention, while incorporating aged manure will enrich the soil with essential nutrients. Always avoid using freshly-manured soil, as it could contain harmful pathogens.
Remember to adequately prepare the soil *before* building your raised bed. This involves removing any existing vegetation, rocks, or debris from the area. This preparation ensures a clean, uniform base that promotes healthy root development. After leveling and amending your chosen soil mix, we advise leaving it to settle for a few days before proceeding with the Timberlake raised bed construction. This allows for optimal settling and prevents future issues caused by soil subsidence. This crucial pre-construction step, often overlooked, contributes significantly to the long-term health and productivity of your garden.
Integrating Your Greenhouse: A Seamless Design

Attaching the Greenhouse Frame: Secure and Weatherproof Connections
Securing your greenhouse to the raised bed requires meticulous planning and execution. In our experience, the most robust connections utilize a combination of methods to withstand varying weather conditions. Simply bolting the greenhouse frame directly to the timber isn’t sufficient; wood expands and contracts with temperature fluctuations, potentially leading to cracks and leaks.
We recommend a three-pronged approach: Firstly, use heavy-duty galvanized brackets designed for outdoor use. These brackets should be strategically placed at multiple points along the greenhouse’s base and secured to the raised bed’s framework with weatherproof screws. Secondly, incorporate a flexible sealant like silicone caulk between the greenhouse frame and the wood to create a waterproof barrier against rain and snow. A common mistake we see is neglecting this step, resulting in water ingress and potential structural damage. Thirdly, consider using weather stripping along the joining points to further improve the seal and prevent air leaks, especially important for maintaining optimal greenhouse temperature.
For example, we’ve found that attaching the greenhouse frame to 4×4 posts embedded into the raised bed corners provides exceptional stability. This sturdy base then allows for easier attachment of the greenhouse frame. Remember to pre-drill all holes to prevent splitting the timber. When choosing your fasteners, prioritize stainless steel or galvanized options to resist corrosion. By combining these techniques—robust brackets, flexible sealant, and weather stripping—you’ll ensure a long-lasting and weatherproof connection between your greenhouse and Timberlake raised garden bed, maximizing its lifespan and functionality.
Choosing the Right Greenhouse Cover: Durability and Light Transmission
The choice of greenhouse covering significantly impacts your Timberlake raised garden bed’s success. In our experience, prioritizing both durability and light transmission is crucial for optimal plant growth. A flimsy cover will tear easily, exposing plants to the elements, while insufficient light transmission will lead to weak, leggy plants. Consider these factors carefully.
Durability varies greatly between materials. Polyethylene film is inexpensive but has a shorter lifespan, typically one to three seasons depending on the quality and UV stabilization. Polycarbonate panels offer superior durability and longevity, often lasting five to ten years or more, while transmitting excellent light. However, they are considerably more expensive. We’ve seen many clients initially opt for polyethylene to save money, only to replace it annually, negating the initial cost savings in the long run. A common mistake we see is underestimating the impact of wind and weather on the greenhouse cover. Always select a material appropriately rated for your region’s climate.
Light transmission is equally vital. While polycarbonate provides excellent light diffusion, some gardeners prefer the sharper light penetration of glass. However, glass is heavy, fragile, and significantly more expensive. Consider the specific light requirements of your chosen plants. For example, shade-loving plants might thrive under a slightly less transparent cover, while sun-worshipping vegetables need maximum light penetration. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for light transmission percentages, factoring this into your overall design and plant selection to ensure a successful harvest from your Timberlake raised garden bed and greenhouse combination.
Ventilation and Temperature Control: Maintaining Optimal Growing Conditions
Maintaining the ideal temperature and airflow within your Timberlake raised garden bed greenhouse is crucial for healthy plant growth. In our experience, neglecting ventilation leads to overheating, which can quickly stress and damage plants, particularly during warmer months. A common mistake we see is relying solely on passive ventilation, which might be insufficient during periods of intense heat. Therefore, a combination of passive and active ventilation strategies is highly recommended.
Passive ventilation, achieved through strategically placed vents or strategically designed greenhouse structures (consider ridge vents or sidewall vents) allows for natural airflow. Remember that the placement and size of these vents significantly influence airflow patterns. For example, higher vents create better stack effect, drawing hot air upwards. However, you might need supplemental active ventilation, such as fans, especially during periods of still air or extreme heat. Consider installing a thermostat-controlled fan system that automatically activates when temperatures exceed a pre-set threshold, ensuring optimal air circulation even when you’re not present. This is particularly important for climate-sensitive crops such as tomatoes and peppers.
Effective temperature management also involves understanding your microclimate. Factors like sunlight exposure, wind patterns, and surrounding landscaping all influence the greenhouse’s internal temperature. Utilizing shade cloth during peak sun hours can dramatically reduce heat buildup. Conversely, supplemental heating during cooler months, whether through electric heaters, propane heaters, or even geothermal systems, becomes essential to maintain consistent growth. Remember to monitor temperatures regularly using reliable thermometers placed at different heights within the greenhouse to capture temperature variations. The goal is consistency – avoiding extreme temperature fluctuations that can stunt growth or invite pest and disease problems.
Planting and Maintenance: tips for Success
Choosing the Right Plants: Ideal Species for Greenhouse Environments
Optimizing your greenhouse environment for specific plant needs is crucial for maximizing yield and minimizing disease. In our experience, selecting plants based solely on aesthetics often leads to disappointment. Instead, prioritize species that thrive in controlled conditions, considering factors like light intensity, humidity, and temperature variations within your Timberlake raised garden beds and greenhouse setup.
For example, tomatoes and peppers, beloved for their adaptability, respond exceptionally well to greenhouse cultivation. They relish the consistent warmth and protection from pests. However, remember proper ventilation is critical to prevent fungal diseases. A common mistake we see is neglecting airflow, leading to damp conditions ideal for blight. Conversely, lettuce and other leafy greens, while generally hardy, might bolt (flower prematurely) if exposed to excessively warm temperatures within the greenhouse. Careful monitoring and shading may be necessary to ensure optimal growth. Consider using shade cloth or strategically positioning your beds.
Ultimately, successful greenhouse gardening hinges on meticulous planning. Before planting, research the specific light, temperature, and humidity requirements for your chosen plants. Experimentation is key; try different species, noting their performance in your unique greenhouse microclimate. We’ve found that keeping detailed records, including planting dates, growth rates, and any pest or disease occurrences, provides invaluable data for future seasons. This iterative process allows you to fine-tune your approach, resulting in a thriving, productive green oasis.
Soil Preparation and Enrichment: Nutrients and Drainage
The foundation of any thriving raised bed garden, especially within a greenhouse environment, is its soil. In our experience, neglecting proper soil preparation leads to stunted growth and reduced yields. Begin by selecting a high-quality soil blend specifically formulated for raised beds. A common mistake we see is using garden soil directly from the ground, which often lacks the necessary drainage and aeration for optimal root development. Look for blends rich in organic matter, like compost and peat moss, to ensure good water retention and nutrient availability.
Enrichment is key. We recommend a soil test before planting to determine your soil’s pH and nutrient levels. This allows for targeted amendment application. For example, a soil low in nitrogen might benefit from the addition of blood meal or composted manure. Phosphorus-deficient soils may require bone meal or rock phosphate. Remember, over-fertilizing is as detrimental as under-fertilizing; always follow package instructions carefully. Consider incorporating slow-release fertilizers for consistent nutrient delivery throughout the growing season.
Drainage is equally crucial, particularly within a greenhouse setting where humidity is often higher. Excellent drainage prevents root rot, a common issue in poorly draining soils. Ensure your raised beds have adequate drainage holes in the bottom. Adding a layer of coarse gravel or broken pottery shards at the base of the bed further improves drainage. For particularly heavy clay soils, consider amending with perlite or vermiculite to increase porosity and aeration. By carefully attending to soil preparation and enrichment, you’ll create the perfect environment for your Timberlake raised bed garden to flourish.
Watering and Fertilizing: Maintaining Optimal Plant Health
Proper watering and fertilization are crucial for thriving plants in your Timberlake raised garden beds. In our experience, consistent moisture is key, especially during the establishment phase. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot and fungal diseases. Instead, water deeply and less frequently, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. A soil moisture meter can be invaluable in determining when to irrigate, preventing both underwatering and overwatering.
Fertilization strategies should be tailored to your specific plants and soil conditions. A soil test before planting will reveal nutrient deficiencies, allowing you to address them proactively. For example, if your test indicates low nitrogen, you might incorporate a slow-release nitrogen fertilizer. We generally recommend using a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 formula, but always follow the package instructions. A common mistake we see is applying too much fertilizer at once, which can “burn” the plants. Opt for smaller, more frequent applications to prevent this.
Consider supplementing with organic matter like compost to improve soil structure and nutrient retention. Compost also enhances water retention, reducing the frequency of watering. For instance, adding a layer of compost to the top of your raised beds every spring will provide a slow release of nutrients throughout the growing season. Remember that consistent monitoring and adjustments to your watering and fertilization regimen are essential throughout the growing season. Regular observation of your plants’ health will help you adapt your approach to optimize growth and yield in your Timberlake greenhouse and raised bed setup.
Troubleshooting Common Problems and Solutions

Dealing with Pests and Diseases: Prevention and Control
Proactive pest and disease prevention is crucial for a thriving Timberlake raised garden bed and greenhouse system. In our experience, neglecting this aspect often leads to significant crop loss. A common mistake we see is relying solely on chemical pesticides, which can harm beneficial insects and disrupt the delicate ecosystem within your greenhouse. Instead, prioritize integrated pest management (IPM), a holistic approach combining preventative measures with targeted interventions.
Implementing IPM starts with choosing disease-resistant varieties when selecting your seeds or seedlings. Regularly inspecting plants for signs of infestation—like holes in leaves, wilting, or unusual discoloration—is vital for early detection. Maintaining good sanitation within your greenhouse is equally important. Remove and properly dispose of infected plants immediately. Avoid overcrowding plants to promote airflow and reduce humidity, which can encourage fungal diseases. Consider beneficial nematodes or ladybugs for natural pest control; these are effective against common garden pests like aphids and slugs.
Beyond biological control, cultural practices play a vital role. Rotating crops annually helps break pest and disease cycles. Proper soil drainage prevents waterlogged conditions that favor fungal growth. We’ve found that using a high-quality soil mix formulated for raised beds, supplemented with compost, significantly enhances plant health and resilience to pests and diseases. Remember, prevention is always the most effective and sustainable strategy in protecting your valuable crops. Early detection and prompt, targeted interventions, informed by sound IPM practices, will keep your Timberlake raised beds and greenhouse thriving.
Addressing Structural Issues: Repairs and Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity of your Timberlake raised garden beds and attached greenhouse. In our experience, neglecting even minor structural issues can lead to significant problems down the line, impacting both the structural integrity and the health of your plants. A common oversight is insufficient foundation preparation. Improper leveling or inadequate drainage can cause settling, warping, and even collapse, especially during periods of heavy rainfall or frost. Always ensure a stable, level base before construction, and consider incorporating a gravel drainage layer.
Addressing structural weaknesses requires prompt action. For minor cracks in the timber, a high-quality wood filler is often sufficient. Larger gaps or splits might necessitate replacing damaged boards. Remember to use exterior-grade wood and appropriate fasteners designed for outdoor use. We’ve found that stainless steel screws are superior to galvanized options for resisting rust and corrosion in damp environments. If significant rot or insect damage is present, replacing affected sections is vital to prevent further deterioration. Failing to address this can compromise the entire structure.
Preventive maintenance is key. Regularly inspect your raised beds and greenhouse for signs of wear and tear, paying close attention to joints, fasteners, and the overall stability. Consider applying a wood preservative every 1-2 years to protect against moisture damage and pest infestations. This will significantly extend the lifespan of your structure. Annual cleaning, including removing debris and weeds, will help maintain a healthy growing environment and allow for early detection of any structural problems. By proactively addressing minor issues, you’ll ensure your Timberlake system remains a productive and beautiful centerpiece of your garden for years to come.
Optimizing Growing Conditions: Temperature, Humidity, and Light
Maintaining optimal growing conditions within your Timberlake raised garden bed and greenhouse is crucial for maximizing yields. In our experience, temperature fluctuations are a significant challenge. A common mistake is neglecting sufficient ventilation, leading to overheating, especially during sunny days. Employ a combination of vents, fans, and shade cloth to regulate temperatures effectively. Aim for daytime temperatures between 65-80°F (18-27°C) and nighttime temperatures no lower than 50°F (10°C) for most vegetables. Using a thermometer placed both inside the greenhouse and within the raised bed itself is highly recommended for accurate monitoring.
Humidity levels are equally important. Excessive humidity can promote fungal diseases, while insufficient humidity can stress plants. Ideal humidity ranges generally fall between 40-70%. Monitoring this requires a hygrometer. Improve air circulation to lower humidity; conversely, misting or using a humidifier can increase it. Remember, humidity requirements differ based on plant species; research the specific needs of your chosen crops. For instance, leafy greens generally prefer higher humidity than tomatoes.
Light is the engine of photosynthesis. Insufficient light will lead to leggy, weak plants, while excessive light can scorch foliage. Your Timberlake setup should receive at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. Supplement with grow lights if necessary, particularly during shorter winter days or in areas with significant shading. Observe your plants carefully for signs of light stress—pale leaves indicate insufficient light, while burnt or yellowed leaves suggest too much. Consider using shade cloth on particularly bright days to prevent sunscald. Regular observation and adjustments based on your specific conditions are key to success.
Showcase Your Creation: Real-World Examples and Inspiration
Stunning Timberlake Raised Garden Bed Designs
Timberlake raised garden beds offer unparalleled versatility in design. In our experience, the key to a stunning design lies in thoughtful planning and material selection. Consider integrating the beds seamlessly into your existing landscape by using matching or complementary materials for pathways and retaining walls. A common mistake we see is neglecting the visual impact of the bed’s height relative to surrounding structures. Taller beds can create a dramatic focal point, while shorter ones blend more subtly into a larger garden.
For a truly exceptional look, experiment with varied bed shapes and sizes. Rectangular beds provide clean lines and efficient space usage, while curved or L-shaped designs add a touch of elegance and can follow the contours of your yard. Consider using contrasting timber types—for example, pairing dark-stained redwood with lighter cedar—to create visual interest. Adding decorative elements like trellises or climbing plants further enhances the aesthetic appeal. One client achieved a breathtaking effect by integrating a small water feature adjacent to their Timberlake beds, creating a calming and inviting ambiance.
Beyond aesthetics, remember practicality. Ensure adequate spacing between beds for easy access and airflow to prevent fungal diseases. We often recommend a minimum of 3 feet between beds, adjustable based on your specific plant choices and access requirements. A well-planned design maximizes sunlight exposure for optimal plant growth. Remember that even the most beautiful Timberlake raised garden bed is ultimately judged on its functionality and ability to produce healthy, thriving plants. Careful consideration of these factors ensures a stunning and productive garden for years to come.
Creative Greenhouse Integration Ideas
Integrating a greenhouse with your Timberlake raised garden beds offers significant advantages, extending the growing season and protecting your plants from harsh weather. In our experience, the most successful integrations prioritize airflow and sunlight maximization. A lean-to greenhouse attached to one side of the bed, for example, provides excellent shelter while still allowing for ample natural light penetration. Consider the prevailing winds in your location when planning placement; a south-facing lean-to is ideal in the Northern Hemisphere for optimal solar gain.
For smaller spaces, a walk-in greenhouse positioned directly over a section of the raised bed is a fantastic solution. This allows for vertical gardening and maximized space utilization. However, a common mistake we see is neglecting proper ventilation. Insufficient airflow can lead to high humidity and disease issues. Incorporate vents strategically – both high and low – to promote air circulation. We’ve found that automatic vents, triggered by temperature sensors, provide optimal climate control and significantly reduce the maintenance burden.
Beyond structural integration, consider creative functional additions. For instance, incorporating a gutter system to collect rainwater for irrigation directly feeds your plants, saving water and reducing your environmental footprint. Similarly, using integrated heating systems inside the greenhouse, such as radiant floor heating or small-scale propane heaters, can extend the growing season further into cooler months, allowing you to experiment with more delicate plants. Remember to carefully assess your budget and energy consumption before committing to these advanced features.
Community Gardening Projects: Sharing Your Expertise
Sharing your expertise with a community gardening project offers numerous benefits beyond just providing growing space. Collaborative projects foster a stronger sense of community and shared responsibility, boosting participation and productivity. Successful projects begin with a clear plan outlining roles, responsibilities, and resources.
Consider structuring your project around themes like heirloom varieties to educate on seed saving and biodiversity, or sustainable practices like composting and rainwater harvesting. Robust communication is crucial; regular meetings, online platforms, and designated leaders help maintain momentum and address challenges. Clearly define access and maintenance responsibilities to avoid conflicts.
Leverage the unique strengths of participants, such as a retired horticulturalist's pruning expertise or a tech-savvy member managing an online resource hub. Collaborating with local schools or organizations can expand your reach and encourage intergenerational learning. Establish clear goals, foster open communication, and harness community knowledge to create a thriving shared garden that showcases the benefits of Timberlake raised garden beds and greenhouses.



Comments